Phys.org February 1, 2024
In the latter half of the twentieth century, a significant climate phenomenon “diurnal asymmetric warming” emerged, wherein global land surface temperatures increased more rapidly during the night than during the day. Recent episodes of global brightening and regional droughts and heatwaves have brought notable alterations to this asymmetric warming trend. An international team of researchers (Sweden, China) re-evaluated sub-diurnal temperature patterns, and revealed a substantial increase in the warming rates of daily maximum temperatures (Tmax) while daily minimum temperatures have remained relatively stable. This shift has resulted in a reversal of the diurnal warming trend, expanding the diurnal temperature range over recent decades. They attributed the intensified Tmax warming to a widespread reduction in cloud cover, leading to increased solar irradiance at the surface. According to the researchers their findings underscore the urgent need for enhanced scrutiny of recent temperature trends and their implications for the wider earth system…. read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
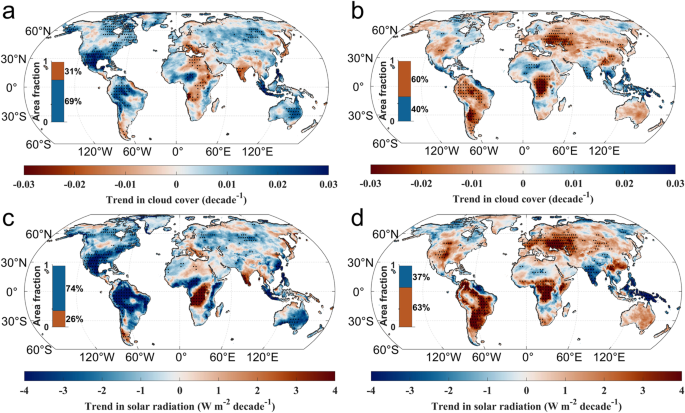
Comparisons of trends in total cloud cover and solar radiation between two periods. Credit: Nature Communications, 08 November 2023