MIT News May 2, 2024
The wavelength of light sets a typical length scale for most experiments to the order of 500 nanometers (nm) or greater. Researchers at MIT implemented a super-resolution technique that localizes and arranges atoms on a sub–50-nm scale, without any fundamental limit in resolution. They demonstrated this technique by creating a bilayer of dysprosium atoms and observing dipolar interactions between two physically separated layers through interlayer sympathetic cooling and coupled collective excitations. At 50-nm distance, dipolar interactions were 1000 times stronger than at 500 nm. According to the researchers for two atoms in optical tweezers, this would enable purely magnetic dipolar gates with kilohertz speed… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
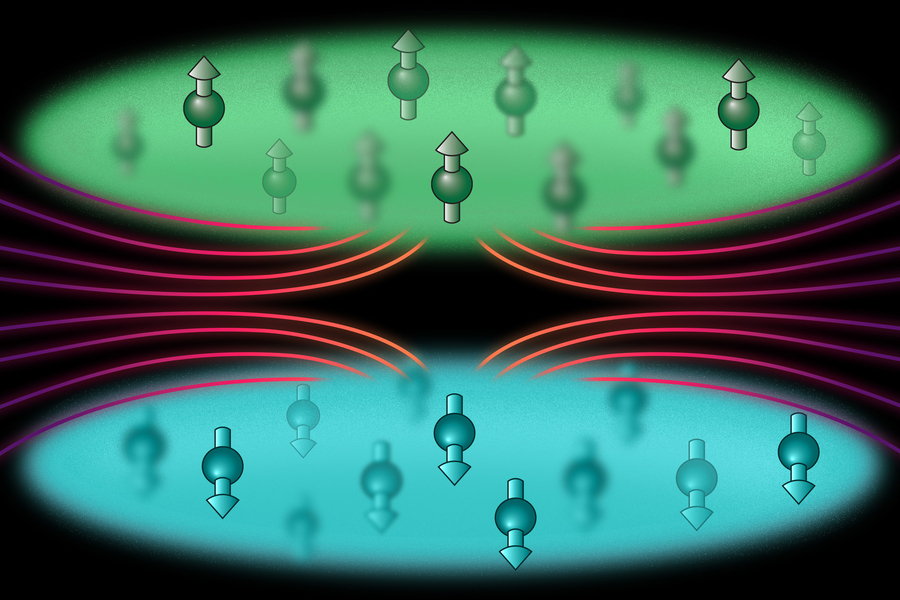
MIT physicists developed a technique to arrange atoms… down to 50 nanometers… Credit: Courtesy of the researchers.