Science Daily September 6, 2023
Lithium-based nonaqueous redox flow batteries (LRFBs) are alternative systems to conventional aqueous redox flow batteries because of their higher operating voltage and theoretical energy density. However, the use of ion-selective membranes limits the large-scale applicability of LRFBs. Researchers at the University of Cincinnati have developed high-voltage membrane-free LRFBs based on an all-organic biphasic system. Under static conditions, these batteries with 0.5 M redox-active material delivered capacity retentions of 98%, 98%, and 92%, respectively, for 100 cycles over ~55 days at the current density of 1 mA/cm2 and a temperature of 27 °C. The battery delivered an initial average cell discharge voltage of 3.45 V and an energy density of ~33 Wh/L, and demonstrated 81% of capacity for 100 cycles over ~45 days with average Coulombic efficiency of 96% and energy efficiency of 82% at the current density of 1.5 mA/cm2 and at a temperature of 27 °C… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
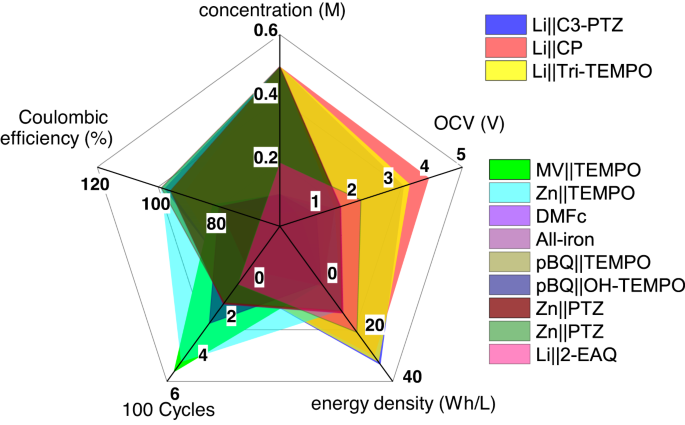
Comprehensive comparison of different battery performances. Credit: Nature Communications volume 14, Article number: 4753 (2023)