Phys.org July 22, 2022
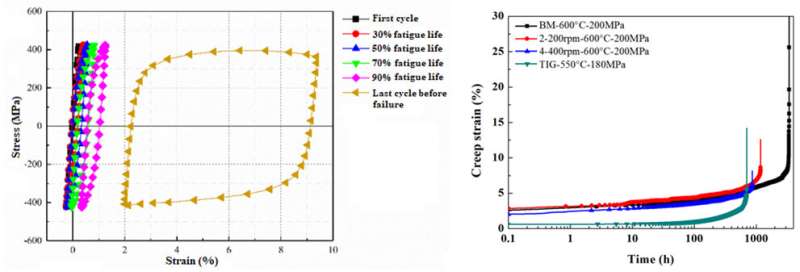
In a review paper a team of researchers in China has introduced the latest development and strategy on fusion energy in China and reviewed the progresses of reduced activation ferritic/martensitic (RAFM) steel for engineering applications. It is considered to be the primary candidate structural material for blankets of ITER, CFETR and DEMO. Several RAFMs have been developed in China (CN-RAFMs) such as CLAM, CLF-1, modified RAFMs and oxide dispersion strengthened RAFMs (ODS-RAFMs). The mechanical properties, irradiation behaviors, additive manufacturing and joining technologies of structural materials have been comprehensively studied. Qualifications of CN-RAFMs are on-going for ITER-TBM fabrication, with emphasis on material property databases and standardization. A new neutron irradiation program is being carried out for a series of fusion materials. Joining technologies and advanced additive manufacturing are performed to overcome the big challenges of the blanket fabrication before ITER, CFETR and DEMO. The databases and standards for CLAM and CLF-1 were established respectively, and the specification and qualification of them are underway for ITER-TBM…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
Fatigue and creep properties of 9Cr-RAFM steels and welded joints. Credit: HFIPS