Phys.org April 4, 2022
The Moon is extremely stable and not influenced by factors on Earth like climate to any large degree. It is a very good calibration reference. An international team of researchers in (US – NIST, USGS, Canada) developed NASA’s airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) which is a telescope that accurately measures how much light is reflected off the lunar surface to assess the amount of energy Earth-observing satellites receive from moonlight. It will help to improve the accuracy and consistency of measurements among Earth-observing satellites. The results will compliment ground-based sites. Scientists can more easily compare data from different satellites to look at global changes over long periods of time. The air-LUSI spectrometer is hermetically sealed within an enclosure that keeps the instrument constantly at sea level temperature and pressure. The team improved the internal monitor so they can better check instrument accuracy from the ultraviolet to the near infrared. They were also able to redesign the integrating sphere to remove small effects of changing temperature leading to 99% measurement accuracy…read more.
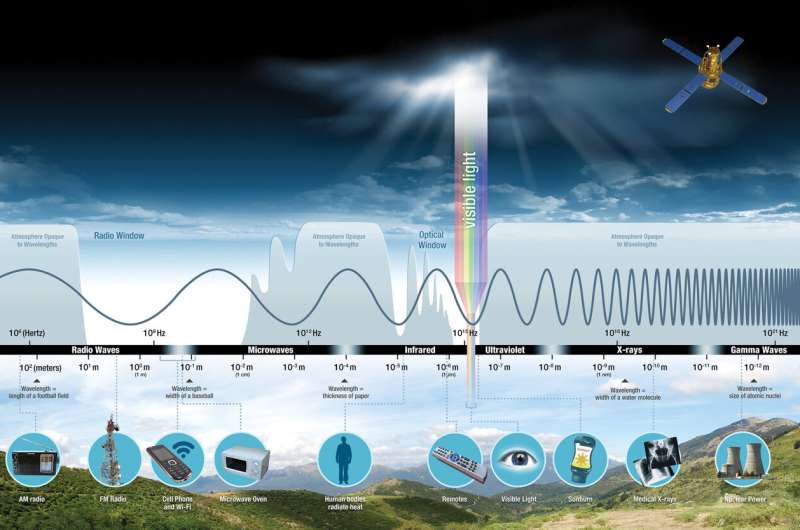
… Humans can only see visible light, but the entire spectrum is used by NASA instruments to observe Earth and more. Credit: NASA