Phys.org January 26, 2022
Traditionally, noise on the quantum device is characterized directly through qubit and gate measurements, but this approach has drawbacks as it does not adequately capture the effect of noise on realistic multi-qubit applications. A team of researchers in the US (University of Chicago, Purdue University) simulated the relaxation of stationary quantum states on a quantum computer to obtain a unique spectroscopic fingerprint of the computer’s noise. In contrast to traditional approaches, they obtained the frequency profile of the noise as it is experienced by the simulated stationary quantum states. Data from multiple superconducting-qubit IBM processors shows that noise generates a bath within the simulation that exhibits both colored noise and non-Markovian behavior. According to the researchers their results provide a direction for noise mitigation but also suggest how to use noise for quantum simulations of open systems… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
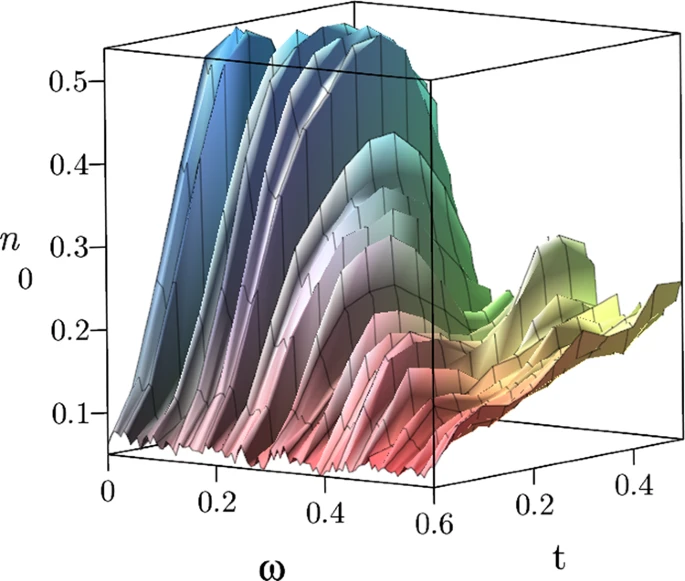
Frequency scan of simulated time evolution for a single qubit. Credit: Communications Physics volume 5, Article number: 28 (2022)