Phys.org August 11, 2021
In 2020 NSF and NASA created the Space Weather with Quantified Uncertainties (SWQU) program. The main change in version 2 was the refinement of the numerical grid in the magnetosphere, several improvements in the algorithms, and a recalibration of the empirical parameters. The Geospace Model provides only about 30 minutes of advanced warning. Researchers at the University of Michigan are working to increase lead time to one to three days. They hope to start from the Sun, using remote observation of the Sun’s surface instead of the current data from a satellite measuring plasma parameters one million miles away from the Earth. A key algorithmic improvement made involved finding a novel way to combine the kinetic and fluid aspects of plasmas in one simulation model they go a million times faster than brute-force simulations by inventing smart approximations and algorithms. The Michigan Sun-to-Earth Model, including the SWMF Geospace and the new GPU port is available as open-source…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
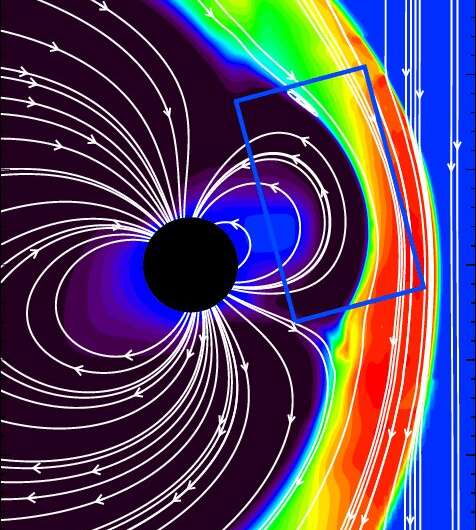
Meridional cut from an advanced three-dimensional magnetosphere simulation….Credit: Chen, Yuxi, et al.