Phys.org July 13, 2021
Oxide-based cathode materials are key components of secondary batteries. Problems originating from the lattice oxygen instability in oxide-based intercalation cathodes are widely reported, such as capacity degradation, gas generation, and thermal runaway, highlighting the importance of deep insights into the critical factors for lattice oxygen stability. Researchers in Japan Investigated the lattice oxygen stability in layered rock-salt LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2−δ with a focus on oxygen release behavior and relevant changes in crystal and electronic structures. Release of lattice oxygen facilitates cation mixing, transition metal slab expansion, and Li slab contraction, thus deteriorating the layered structure. In the beginning stage of oxygen release, the charge balance is compensated by selective reduction of Ni3+. This strongly suggests that high valent Ni generated by delithiation or negative defect species, that is, lithium at the transition metal site ( Li″ TM), aggravates oxygen release severely. These findings provide a new research direction and guidelines for the stabilization of lattice oxygen in oxide-based intercalation cathodes…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
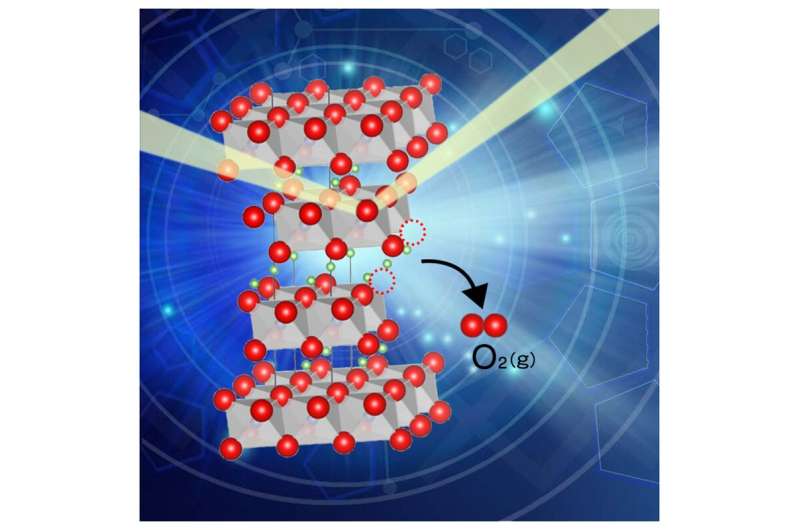
Oxygen release from battery materials which can cause thermal runaway. Credit: Takashi Nakamura