Nanowerk May 31, 2021
For successful implementation of photoelectrocatalytic synthesis of fuels and value-added chemicals hybrid photoelectrodes with low energy consumption and high photocurrent densities are essential. Researchers in Japan have developed a laser-driven technology to print sensitizers with desired morphologies and layer thickness onto different substrates, such as glass, carbon, or carbon nitride (CN). The process uses a thin polymer reactor impregnated with transition metal salts, confining the growth of TMO nanostructures on the interface in milliseconds, while their morphology can be tuned by the laser. Multiple nano-p-n junctions at the interface increase the electron/hole lifetime by efficient charge trapping. A hybrid copper oxide/CN photoanode with optimal architecture reaches 10 times higher photocurrents than the pristine CN photoanode. This technology provides a modular approach to build a library of TMO-based composite films, enabling the creation of materials for diverse applications…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
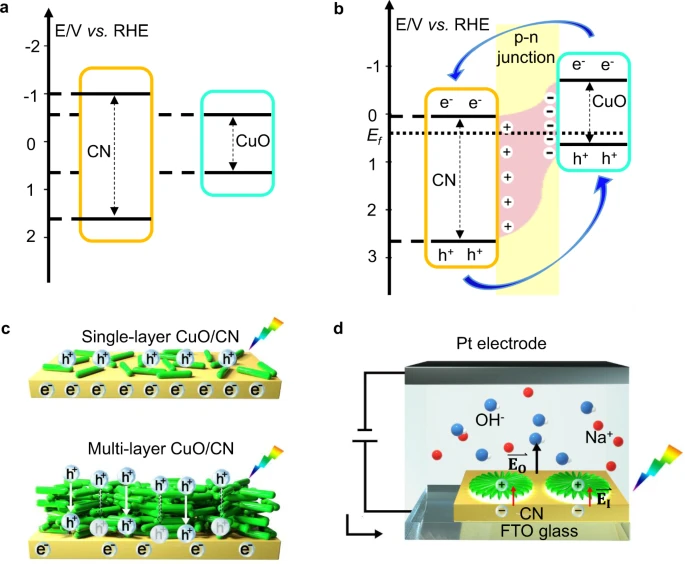
Energy diagrams of the materials and charge transport properties. Credit: Nature Communications volume 12, Article number: 3224 (2021)