Science Daily May 18, 2021
Researchers in Sweden have developed a rechargeable cement-based battery using iron and zinc as anodes, and nickel-based oxides as cathodes. The conductivity of cement-based electrolytes was modified by adding short carbon fibers. The electrodes were produced by two methods: powder-mixing and metal-coating. Different combinations of cells were tested. The results showed that the best performance of the rechargeable battery was the Ni–Fe battery, produced by the metal-coating method. The battery has an average energy density of 7 Wh/m2 (or 0.8 Wh/L) during six charge/discharge cycles. Their battery could be more than ten times that of earlier attempts at concrete batteries. The energy density is still low in comparison to commercial batteries, but this limitation could be overcome thanks to the huge volume at which the battery could be constructed when used in buildings. The idea is still at a very early stage. The technical questions remaining to be solved before commercialization of the technique can be a reality include extending the service life of the battery, and the development of recycling techniques…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
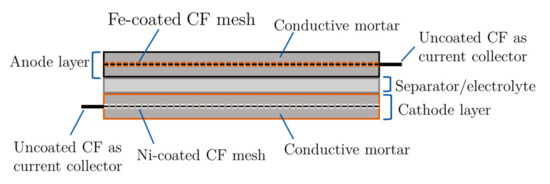
Schematic illustration of the design of the metal-coating battery. Credit: Buildings 2021, 11(3), 103