Phys.org February 7, 2024
Quantum repeater networks require independent absorptive quantum memories capable of storing and retrieving indistinguishable photons to perform high-repetition entanglement swapping operations. An international team of researchers (USA – Stony Brook University, industry, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Italy) performed Hong-Ou-Mandel (HOM) interference between photonic polarization states and single-photon-level pulses stored and retrieved from two sets of independent room-temperature quantum memories. They showed that the storage and retrieval of polarization states from quantum memories did not degrade the HOM visibility for few-photon-level polarization states in a dual-rail configuration. For single-photon-level pulses, they measured the HOM visibility with various levels of background in a single polarization, single-rail QM, and investigated its dependence on the signal-to-background ratio. They obtained a HOM visibility of 43%, compared to the 48% no-memory limit of their set-up. They estimated a 33% visibility for polarization qubits under the same conditions. According to the researchers their demonstrations lay the groundwork for future applications using large-scale memory-assisted quantum networks… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
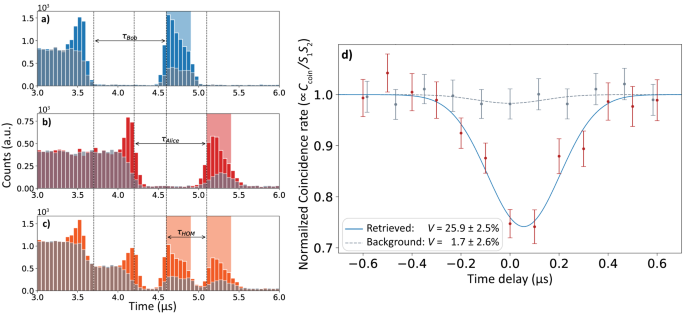
HOM interference of pulses retrieved from two quantum memories… Credit: npj Quantum Information volume 10, Article number: 10 (2024)