Nanowerk September 16, 2023
Ferroelectricity in binary oxides including hafnia and zirconia is interesting because of their unconventional physical mechanisms and the potential for the integration of these materials into semiconductor workflows. Behaviors such as wake-up phenomena and an extreme sensitivity to electrode and processing conditions suggest that ferroelectricity in these materials is strongly influenced by other factors, including electrochemical boundary conditions and strain. An international team of researchers (USA – Oak Ridge National Laboratory, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, Carnegie Mellon University, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Ukraine) argued that the properties of these materials emerge due to the interplay between the bulk competition between ferroelectric and structural instabilities, similar to that in classical antiferroelectrics, coupled with non-local screening mediated by the finite density of states at surfaces and internal interfaces. They showed that these materials demonstrated a rich spectrum of ferroic behaviors including partial-pressure-induced and temperature-induced transitions between ferroelectric and antiferroelectric behaviors which are consistent with an antiferroionic model and suggested strategies for hafnia-based device optimization… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
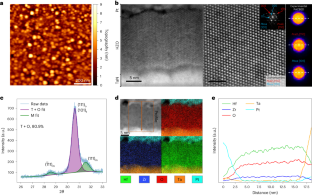
Structural and chemical characterization of HZO. Credit: Nature Materials volume 22, pages1144–1151 (2023)