Phys.org July 24. 2023
Researchers in China introduced platinum–rare earth metal-based alloy catalyst, Pt2Gd, to reveal the role of spin configurations in the catalytic activity of materials. The catalyst exhibited a unique intrinsic spin reconfiguration because of interactions between the Gd-4f and Pt-5d orbitals. The adsorption and desorption of the oxygen species were optimized by modifying the spin symmetry and electronic structures of the material for increased oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) efficiency. The Pt2Gd alloy exhibited a half-wave potential, and a superior mass activity, and higher durability than conventional Pt/C catalysts. Theoretical calculations have proved that the spin shielding effect of the Gd pairs increases the spin symmetry of the Pt-5d orbitals and the adsorption preferences toward spin-polarized intermediates to facilitate ORR. According to the researchers their work clarifies the effect of modulating the local high spin 4f orbital electrons in rare earth metals to enhance its ORR performance… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE (accepted manuscript)
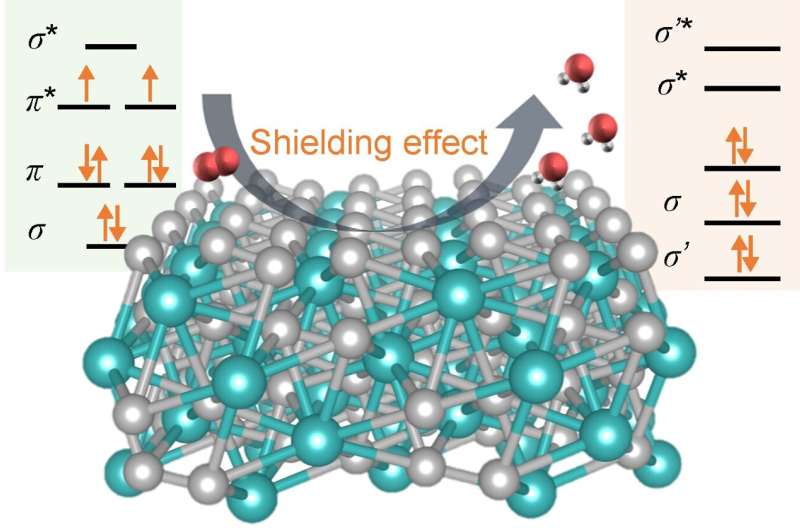
Schematic diagram of the Spin shielding effect in oxygen electrocatalysis… Credit: Science China Press