Phys.org December 6, 2022
In antiferromagnets, the efficient transport of spin-waves has until now only been observed in the insulating antiferromagnet hematite, where circularly polarized spin-waves diffuse over long distances. An international team of researchers (Germany, France, Norway, China) observed long-distance spin-transport in the antiferromagnetic orthoferrite YFeO3, where a different transport mechanism was enabled by the combined presence of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction and externally applied fields. The magnon decay length exceeded hundreds of nanometers, in line with resonance measurements that highlight the low magnetic damping. They observed a strong anisotropy in the magnon decay lengths which they attributed to the role of the magnon group velocity in the transport of spin-waves in antiferromagnets. According to the researchers this mode of transport identified in YFeO3 opens the possibility of a large and technologically relevant class of materials for long-distance spin transport…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
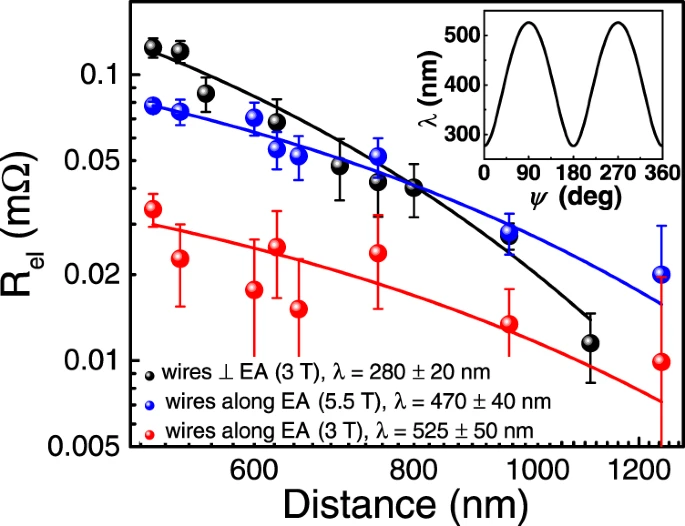
Distance dependence of spin transport signal at 200 K. Credit: Nature Communications volume 13, Article number: 6140 (2022)