Phys.org September 6, 2021
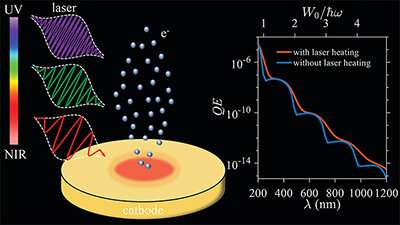
Researchers at Michigan State University performed a comprehensive theoretical analysis of photoemission from metal surfaces due to laser illumination ranging from ultraviolet wavelengths of 200 nanometers to near-infrared wavelengths of 1200 nanometers. By analyzing photoemission mechanisms, current density, and quantum efficiency for this range of wavelengths, they found the electron emission mechanism varies depending on the laser wavelength, laser intensity and DC bias field. The calculations showed quantum efficiency can be nonlinearly increased through electron heating produced by intense sub-picosecond laser pulses, emphasizing the importance of laser heating. Quantum efficiency increased the most at laser wavelengths where the cathode work function was close to an integer multiple of the laser photon energy. The results could help guide the development of highly efficient and bright photoelectron sources…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE 1 2
Peng Zhang and Yang Zhou are working to improve the quantum efficiency of photoemission. Credit: Michigan State University