Phys.org February 8, 2021
Wiring up the transistors of an optical circuit with silicon waveguides is an important requirement to make compact, highly integrated chips. However, silicon is a strong absorber of visible light. To circumvent the absorption issue researchers in Switzerland used high contrast grating consisting of nanometer sized “posts” lined up in such a way that light passing through the posts interferes destructively with light passing between posts making sure that no light can “leak” through the grating. Most of the light gets reflected inside the waveguide. They showed that there was a loss of only 13 percent along a light travel path of 1 millimeter inside the waveguide. According to the researchers low-loss silicon waveguide could enable new photonic chip designs for use in biosensing and other applications that rely on visible light and optical components such as lasers and modulators widely used in telecommunications…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
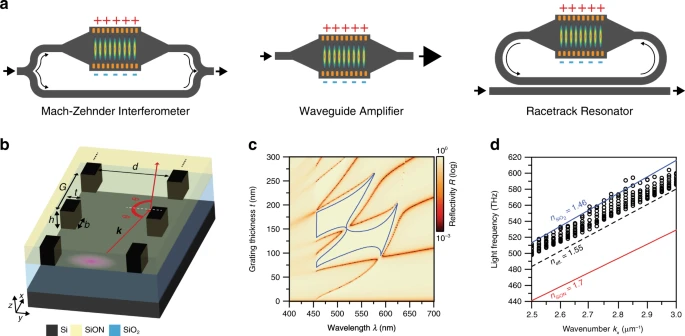
Light reflection from an HCG and waveguiding. Credit: Light: Science & Applications volume 10, Article number: 15 (2021)