Phys.org September 9, 2020
Monazite–(Ce) is a common accessory rock component that bears petrogenetic information, which is widely used in geochronology and thermochronology, and is considered a potential host material for immobilization of radioactive waste. An international team of researchers (Austria, Germany, Russia, Czech Republic) conducted an ion-irradiation study that has unraveled the causes of the self-healing of monazite. They found that only in radiation-damaged monazite–(Ce), 4He ions cause gradual structural restoration. In contrast, its high-temperature annealed analogue and synthetic CePO4 experience He-irradiation damage. Alpha-assisted annealing contributes to preventing irradiation-induced amorphization of monazite–(Ce); however, this process is only significant above a certain damage level…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
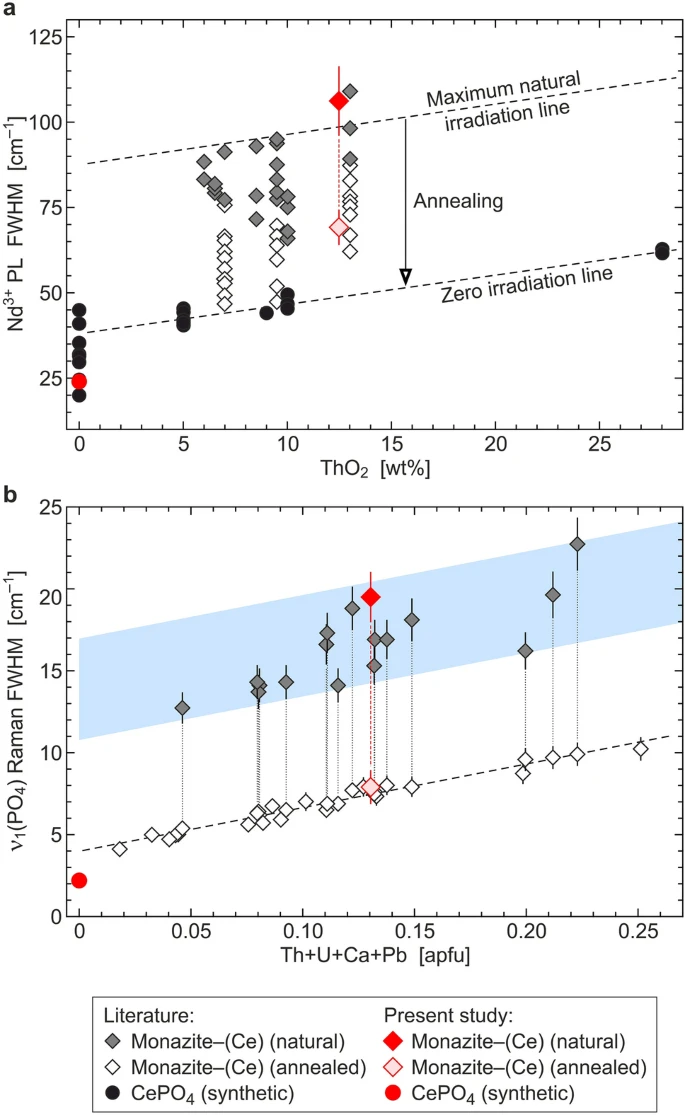
Spectroscopy-based estimation of radiation damage in monazite–(Ce)…. Credit: Scientific Reports volume 10, Article number: 14676 (2020)