Science Daily April 20, 2020
Fish farmers use large quantities of antimicrobials to treat or prevent disease on their farms. However, when used inappropriately, antimicrobials are ineffective and foster the development of resistant bacteria. An international team of researchers (France, Germany) conducted a double meta-analysis to explore how global warming and antimicrobial resistance impact aquaculture. They calculated a Multi-Antibiotic Resistance index (MAR) of aquaculture-related bacteria for 40 countries. They showed that aquaculture MAR indices correlate with MAR indices from human clinical bacteria, temperature and countries’ climate vulnerability and infected aquatic animals present higher mortalities at warmer temperatures. They raise the alarm about the consequences of inappropriate antibiotic use. Resistant bacteria in aquaculture can either spread or transmit their resistance genes to non-resistant bacteria that infect humans, thus causing diseases that are difficult to treat in both animals and humans…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
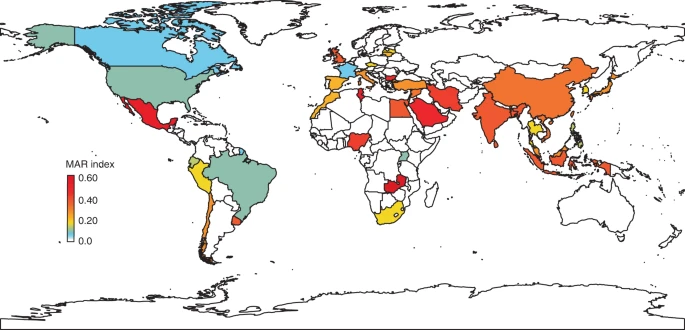
Global multi-antibiotic resistance (MAR) index calculated from aquaculture-derived bacteria. Credit: Nature Communications volume 11, Article number: 1870 (2020)