Phys.org June 26, 2024
The current concrete carbonation approaches are hindered by low CO2 capture efficiency and high energy consumption, often resulting in weakened concrete. An international team of researchers (USA – Northwestern University, Switzerland) experimentally explored a carbonation approach that resorts to injecting CO2 into a cement suspension subsequently used to manufacture concrete, turning the carbonation reaction into an aqueous ionic reaction with a very fast kinetics compared to traditional diffusion-controlled approaches. This approach achieved a CO2 sequestration efficiency of up to 45% and maintained an uncompromised concrete strength. The study showed that the CO2 injection rate influenced the polymorph selectivity of mineralized calcium carbonate depending on the local environmental conditions, and impacted the strength of concrete. According to the researchers the proposed approach enables a reduced carbon footprint and promising prospects for industrial implementation… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
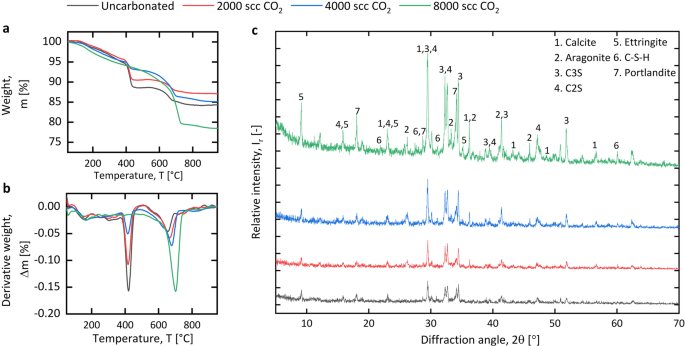
Characterization of carbonated and uncarbonated cement suspensions. Credit: Communications Materials volume 5, Article number: 109 (2024)