Phys.org February 1, 2024
An international team of researchers (Germany, USA, Switzerland, UK) studied the time evolution of lattice fluctuations in the quantum paraelectric SrTiO3, in which mid-infrared drives have been shown to induce a metastable ferroelectric state. Crucial in these physics is the competition between polar instabilities and antiferrodistortive rotations, which in equilibrium frustrate the formation of long-range ferroelectricity. They made use of high-intensity mid-infrared optical pulses to resonantly drive the Ti–O-stretching mode at 17?THz, and measured the resulting change in lattice fluctuations using time-resolved X-ray diffuse scattering at a free-electron laser. They observed a long-lived quench in R-point antiferrodistortive lattice fluctuations. Their enhancement and reduction were theoretically explained by considering the fourth-order nonlinear phononic interactions to the driven optical phonon and third-order coupling to lattice strain, respectively. These observations provided a number of testable hypotheses for the physics of light-induced ferroelectricity… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
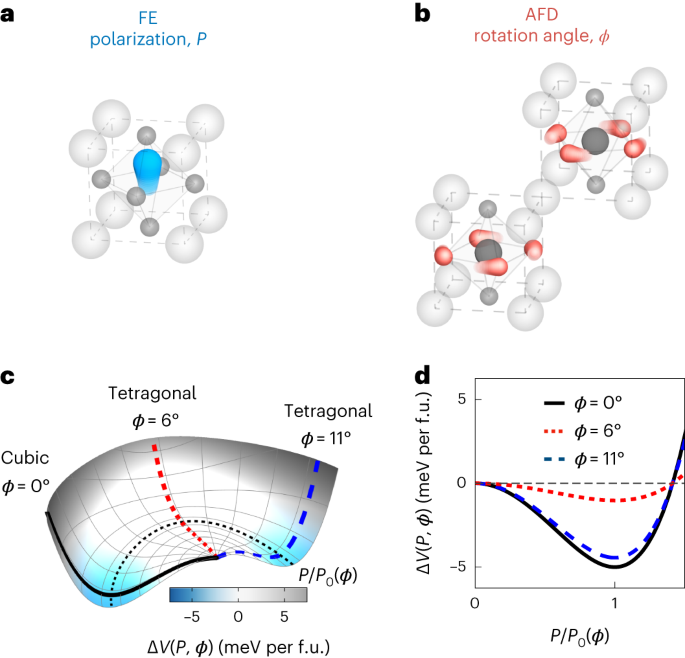
Fundamental distortions of STO. Credit: Nature Materials, 01 February 2024