Nanowerk February 21, 2024
Research has predominantly focused on inorganic cation perovskite-based colloidal quantum dots (PQDs) even though organic cation PQDs have more favorable bandgaps. Researchers in South Korea developed solar cells using narrow bandgap organic cation based PQDs and demonstrated substantially higher efficiency compared with their inorganic counterparts. They employed an alkyl ammonium iodide-based ligand exchange strategy, which proved to be substantially more efficient in replacing the long-chain oleyl ligands than conventional methyl acetate-based ligand exchange while stabilizing the α phase of organic PQDs in ambient conditions. They showed a solar cell with the organic cation PQDs with high certified quasi-steady-state efficiency of 18.1% with 1,200-h stability under illumination at open-circuit conditions and 300-h stability at 80 °C. According to the researchers their study presents a new direction for the ligand exchange method in organic PQDs, serving as a catalyst to revolutionize the field of QD solar cell material research in the future… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
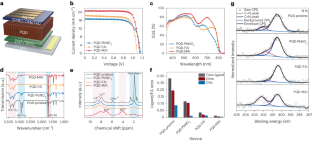
Photovoltaic performance and surface characteristics… Credit: Nature Energy, 26 January 2024