Nanowerk February 2, 2024
Although metallic nanostructures are interesting for nanoscience and nanotechnologies, environmental attacks on them can easily initiate cracking on the surface of metals deteriorating their overall functional/structural properties. An international team of researchers (China, Hong Kong, Taiwan) shown that severely oxidized metallic glass nanotubes can attain an ultrahigh recoverable elastic strain at room temperature. They showed that the physical mechanisms underpinning the observed superelasticity could be attributed to the formation of a percolating oxide network in metallic glass nanotubes, which not only restricts atomic-scale plastic events during loading but also leads to the recovery of elastic rigidity on unloading. According to the researchers their discovery implies that oxidation in low-dimensional metallic glasses can result in unique properties for applications in nanodevices… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
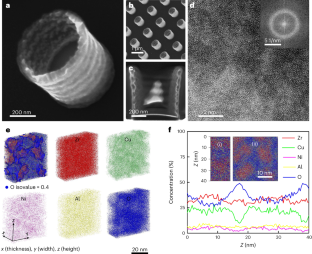
Structural and compositional characterizations … Credit: Nature Materials volume 23, pages52–57 (2024)