MIT News September 6, 2023
Researchers at MIT have designed, evaluated, and implemented Van Atta Acoustic Backscatter (VAB), a technology that enables long-range, ultra-low-power networking in underwater environments. VAB is scalable underwater backscatter architecture that bridges recent advances in RF backscatter (Van Atta architectures) with ultra-low-power underwater acoustic networks. Their design introduces multiple innovations across the networking stack to overcome unique challenges that arise from the electro-mechanical properties of underwater backscatter and the challenging nature of low-power underwater acoustic channels. They implemented and evaluated their design in over 1,500 real-world experimental trials in a river and the ocean. In stationary setups VAB achieved a communication range that exceeded 300m in round trip backscatter across orientations (at BER of 10−3). In comparison with the past state of the art systems VAB showed a 15× improvement in communication range at the same throughput and power. By realizing hundreds of meters of range in underwater backscatter, their presents the first practical system capable of coastal monitoring applications… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
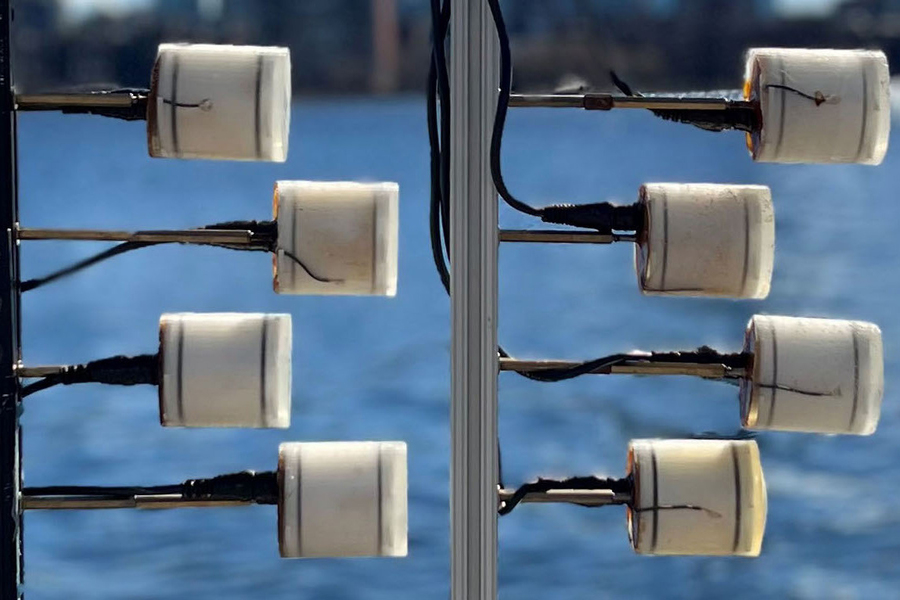
… array of piezoelectric transducers that enables battery-free underwater communication. Credit: The researchers.