Science Daily July 11, 2023
Autonomous lander missions on extraterrestrial bodies will need to sample granular material while coping with domain shift, no matter how well a sampling strategy is tuned on Earth. Researchers at the University of Illinois proposed an adaptive scooping strategy that uses deep Gaussian process method trained with meta-learning to learn on-line from very limited experience on the target terrains. Deep Meta-Learning with Controlled Deployment Gaps (CoDeGa) explicitly trained the deep kernel to predict scooping volume robustly under large domain shifts. Employed in a Bayesian Optimization sequential decision-making framework, the proposed method allowed the robot to use vision and very little on-line experience to achieve high-quality scooping actions on out-of-distribution terrains, significantly outperforming non-adaptive methods proposed in the excavation literature as well as other state-of-the-art meta-learning methods. The researchers made available a dataset of 6,700 executed scoops collected on a diverse set of materials, terrain topography, and compositions for future research in granular material manipulation and meta-learning… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
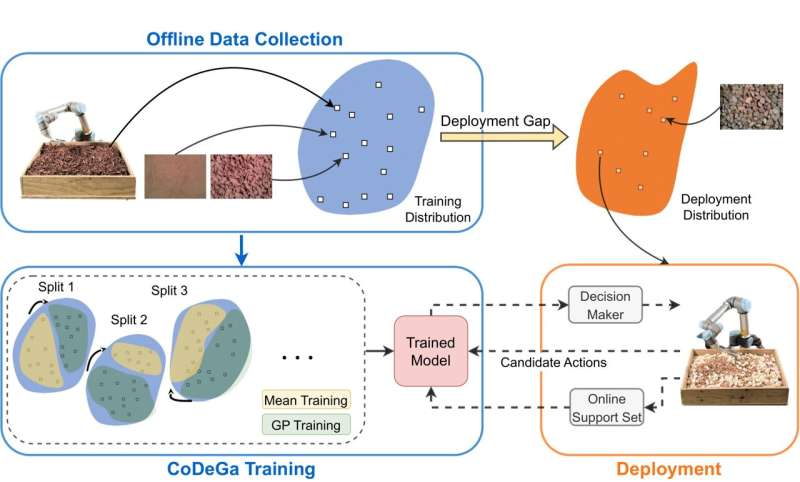
The proposed deep Gaussian process model is trained on the offline database with deep meta-learning… Credit: University of Illinois Dept. of Aerospace Engineering.