Science Daily June 27, 2023
Magnetotactic bacteria contain magnetosomes, iron crystals wrapped in a membrane, which arrange themselves to align with the Earth’s magnetic field, causing the bacteria to travel in the direction of Earth’s magnetic field lines leading north or south. Magnetosome-producing microorganisms can sense and move toward the redox gradient. Researchers in Japan collected a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney. The mineralogical and geochemical characterization of the vent chimney sample showed an internal iron redox gradient. The electron microscopy of particles collected from the chimney sample revealed magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) cells with bullet-shaped magnetosomes, and there were minor occurrences of cuboctahedral and hexagonal prismatic magnetosomes. They performed Genome-resolved metagenomic analysis to identify microorganisms that formed magnetosomes. A metagenome-assembled genome (MAG) affiliated with Nitrospinae had magnetosome genes. A diagnostic feature of MTB genomes, such as magnetosome gene clusters (MGCs) was also confirmed in the Nitrospinae-affiliated MAG. Two lines of evidence support the occurrence of MTB in a deep-sea, inactive hydrothermal vent environment. According to the researchers their work shows that the magnetic bacteria might be found in yet more unexpected locations, on Earth and perhaps even on Mars or beyond… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
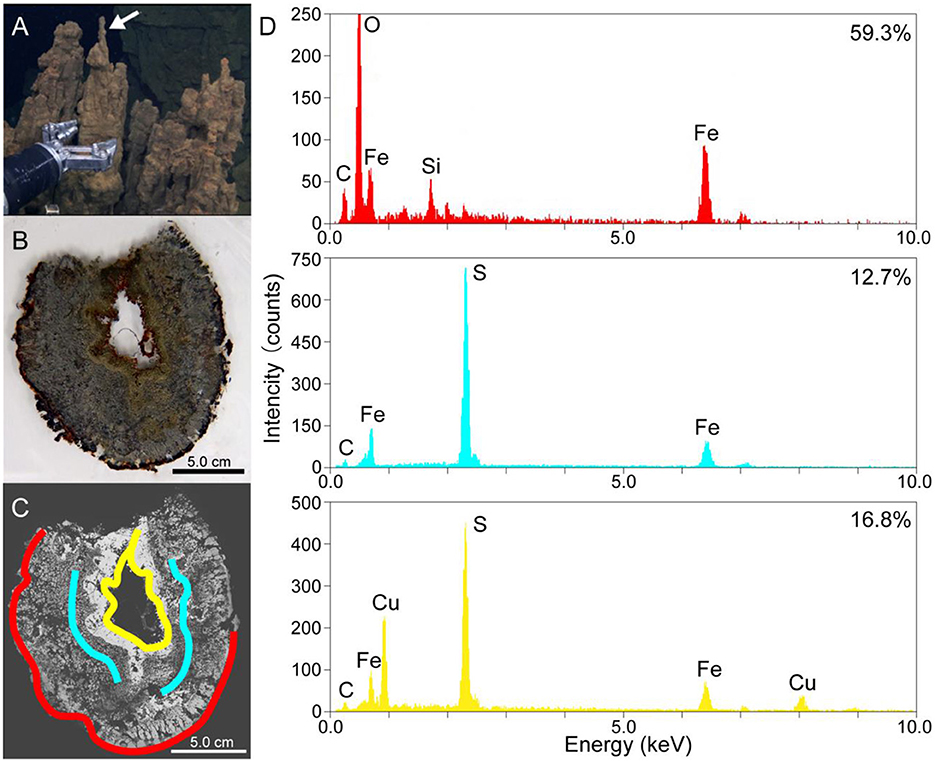
(A) A photo of the metal sulfide chimney collected from the Pika site… Credit: Front. Microbiology, 27 June 2023