Phys.org March 24, 2023
Whereas ultracold atoms and superconducting circuits have since taken independent paths in the exploration of new physics, taking advantage of their complementary strengths in an integrated system enables access to fundamentally new parameter regimes and device capabilities. Taking advantage of their complementary strengths in an integrated system a team of researchers in the US (University of Chicago, Stanford University) developed a system, coupling an ensemble of cold 85Rb atoms simultaneously to an optically accessible, three-dimensional superconducting resonator and a vibration-suppressed optical cavity in a cryogenic (5 K) environment. To demonstrate the capabilities of the platform, they leveraged the strong coupling between Rydberg atoms and the superconducting resonator to implement a quantum-enabled millimetre wave photon to optical photon transducer. They measured internal conversion efficiency of 58(11)%, a conversion bandwidth of 360(20) kHz and added thermal noise of 0.6 photons, in agreement with a parameter-free theory. According to the researchers this will allow near-unity efficiency transduction in both the mmwave and microwave regimes. Their results open a new field of hybrid mmwave/optical quantum science, with prospects for operation deep in the strong coupling regime for efficient generation of metrologically or computationally useful entangled states and quantum simulation/computation with strong non-local interactions… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
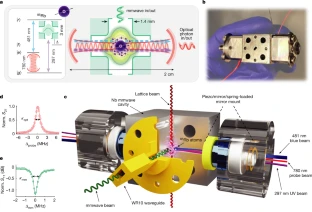
Experimental setup. Credit: Nature volume 615, pages 614–619 (2023)