Phys.org January 23, 2023
Researchers in China constructed two heterometallic clusters to improve the solar absorption and performance of titanium oxo clusters. Their studies indicated that these structures exhibited enhanced visible-light absorption and significantly reduced optical band gaps which could be mainly attributed to the introduction of electron-rich molybdenum (Mo) pairs as heterometals. They found that the electron-rich Mo–Mo pairs could be introduced to titanium oxo clusters to enhance visible-light absorption. They attributed the reduction in the band gaps to the introduction of electron-rich Mo-Mo pairs as heterometals. They also found that the bands shift effectively toward the visible-light region. According to the researchers their work has potential applications in the field of solar energy where solar conversion currently faces certain limitations…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
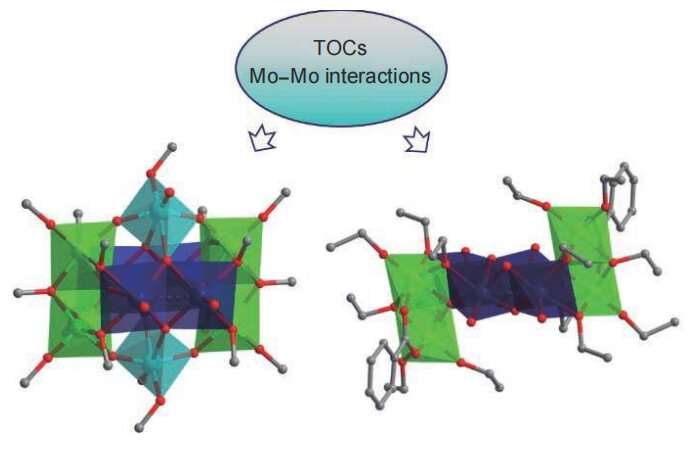
Polyhedral models showing the molecular structure of the two heterometallic clusters… Credit: Polyoxometalates, Tsinghua University Press