Phys.org November 8, 2022
Although considerable progress has been made in CO2 electroreduction, sustained production of multicarbon compounds at high current density remains a challenge. Researchers in China reported a hierarchical micro/nanostructured Cu(100)-rich copper hollow fiber as a gas penetration electrode (GPE) that reduces CO2 to C2+ product with a faradaic efficiency of 62.8% and a current density of 2.3 A cm-2 in 0.5 M KHCO3 solution at −1.94 V (vs. RHE). Electrochemical results demonstrate that optimized mass transfer and enhanced three-phase interface reaction synergistically promote CO2 activation and reduction kinetics. Theoretical calculations suggested that the Cu(100) facet of Cu GPE favors CO intermediate adsorption and then facilitates C-C coupling, resulting in selective C2+ product formation…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
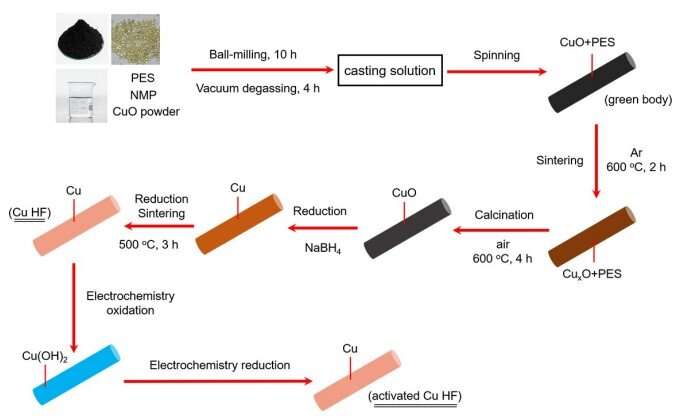
Schematic illustration showing the general procedures for the fabrications of Cu HF and activated Cu HF. Credit: Energy & Environmental Science (2022).