Phys.org October 12, 2022
A team of researchers in the US (Pennsylvania State University, Argonne National Laboratory, NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies, New York, Texas A&M, College Station) developed the Earth Model Column Collaboratory (EMC2), an open-source ground-based lidar and radar instrument simulator and subcolumn generator, specifically designed for large-scale models, in particular climate models, but also applicable to high-resolution model output. It provides a flexible framework enabling direct comparison of model output with ground-based observations, including generation of subcolumns that may statistically represent finer model spatial resolutions and EMC2 large-scale models’ physical assumptions implemented in their cloud or radiation schemes. The team presented a case study of highly supercooled mixed-phase cloud based on measurements from the US DOE’s Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) West Antarctic Radiation Experiment (AWARE). We compared observations with the application of EMC2 to outputs from four configurations. They showed that two of the four ModelE3 configurations can form and maintain highly supercooled precipitating cloud for several hours, consistent with observations and LES. ModelE3 configurations, and the LES results post-processed with EMC2 generally provide reasonable agreement with observed lidar and radar variables…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
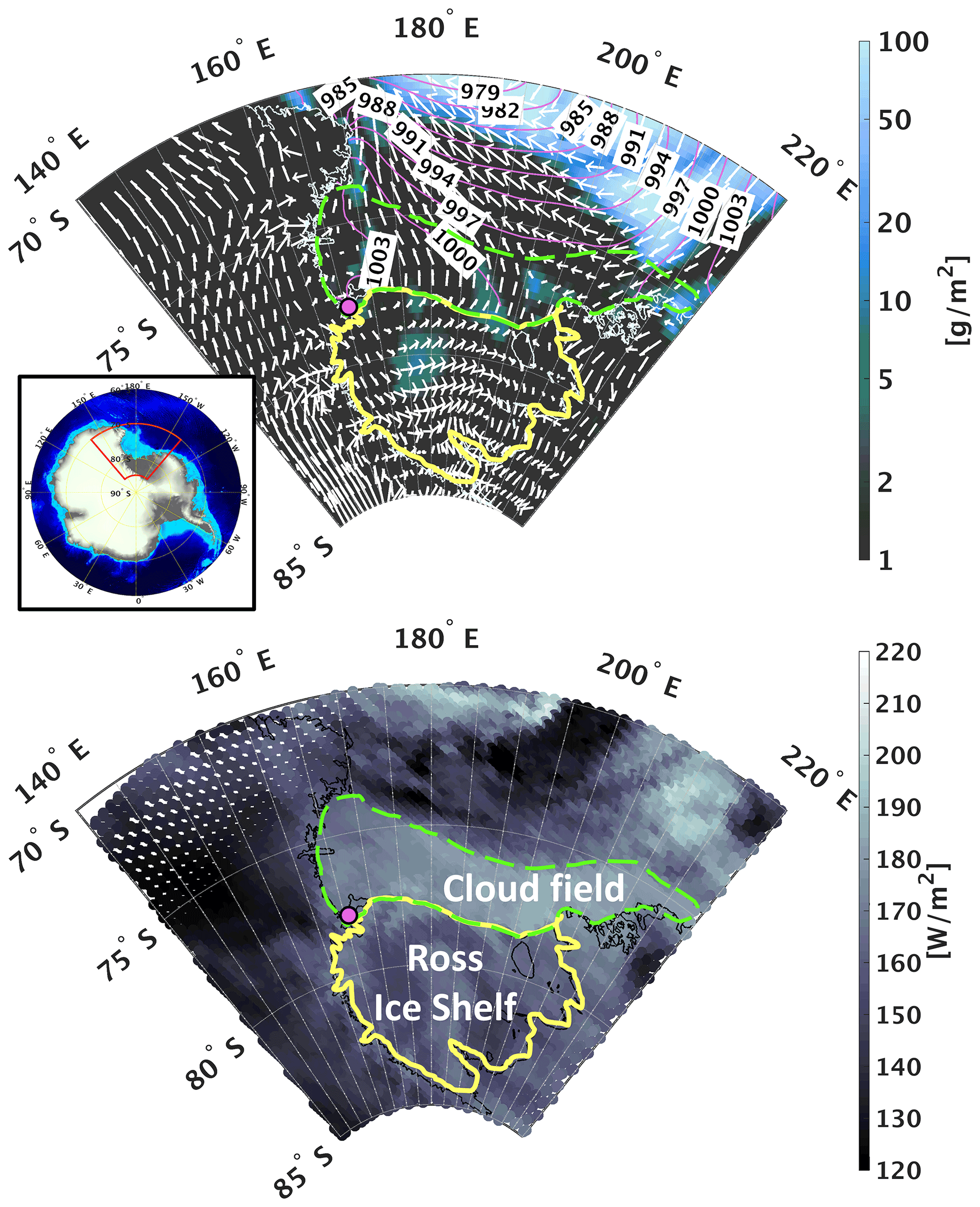
Sea level pressure, total condensate water path, and surface winds (quivers) resolved by ERA5…Credit: Geosci. Model Dev., 15, 901–927, 2022