Phys.org September 1, 2022
Force chains are quasi-linear self-organised structures carrying large stresses and are ubiquitous in jammed amorphous materials like granular materials, foams or even cell assemblies. Understanding force chains is crucial in describing the mechanical and transport properties of granular solids and this applies in a wide range of circumstances—for example how sound propagates or how sand responds to mechanical deformation. Predicting where they will form upon deformation is crucial to describe the properties of such materials but remains an open question. An international team of researchers (Germany, Belgium, UK) demonstrated that graph neural networks (GNN) can accurately predict the location of force chains in both frictionless and frictional materials from the undeformed structure, without any additional information. By analyzing the structure of the force chains, they identified the key features that affect prediction accuracy. According to the researchers their results and methodology will be of interest for granular matter and disordered systems, e.g., in cases where direct force chain visualization or force measurements are impossible…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
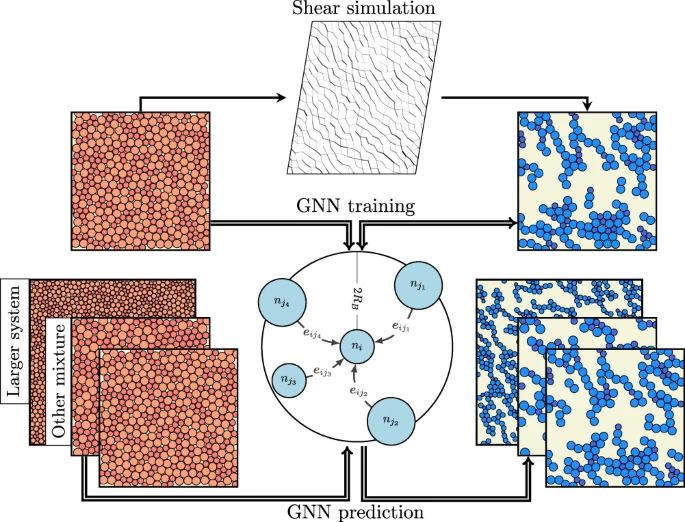
Schematic of our method for predicting the formation of force chains. Credit: Nature Communications volume 13, Article number: 4424 (2022)