Phys.org May 13, 2022
Chip-integrated two-dimensional material photodetectors implemented with the configuration of metal-semiconductor-metal suffer from high dark currents and low responsivities at high operation speed. An international team of researchers (China, Belgium, Spain, Finland) has developed a van der Waals PN heterojunction photodetector, composed of p-type black phosphorous and n-type molybdenum telluride, integrated on a silicon nitride waveguide. The built-in electric field of the PN heterojunction significantly suppresses the dark current and improves the responsivity. The dark current is lower than 7 nA, which is more than two orders of magnitude lower than those reported in other waveguide-integrated black phosphorus photodetectors. The van der Waals PN heterojunction is tunable by the electrostatic doping to further engineer its rectification and improve the photodetection, enabling an increased responsivity. The heterojunction photodetector exhibits a response bandwidth of ~1.0 GHz and a uniform photodetection over a wide spectral range, as experimentally measured from 1500 to 1630 nm. According to the researchers their work has the potential to develop high-performance on-chip photodetectors… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
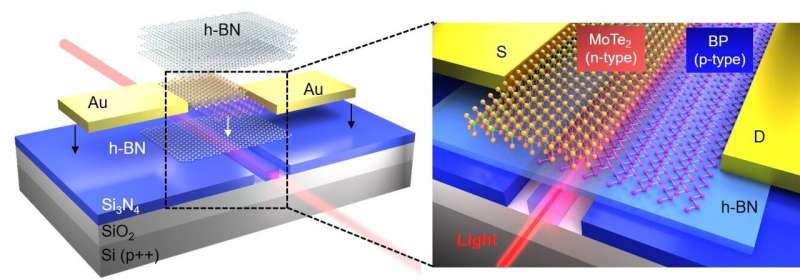
Credit: Ruijuan Tianv…