Nanowerk April 18, 2022
Until now, studies on wireless energy transfer (WET) have been mainly based on the electromagnetic (EM) induction method using EM waves. However, it is still challenging to utilize current EM wave mediated WET in those areas where it is most needed: underwater, body-implant, and EM-shielded cases (liquid/metals). Researchers in South Korea have developed a triboelectric acoustic energy transfer (AET) module by tuning the work function of the triboelectric layer via the large polarization of the embedded relaxor single crystal. The uniform displacement, a quasi-mode oscillation, across the flexible electrode surface in response to the square wave has improved energy transfer efficiency. They demonstrated the transmission of 8 mW electric power at 6 cm underwater. They demonstrated AET in both liquids (underwater and in-body), and solids (metal, wood, and plastic). According to the researchers their approach will enable AET technology to be utilized in the actual field…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
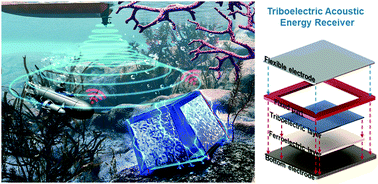
Triboelectric Acoustic Energy Reveiver. Credit: Energy Environ. Sci., 2022,15, 1243-1255