Phys.org January 10, 2022
The problem of optimizing over random structures emerges in many areas of science and engineering, ranging from statistical physics to machine learning and artificial intelligence. For many such structures, finding optimal solutions by means of fast algorithms is not known and often believed impossible to solve. At the same time, the formal hardness of these problems in the form of the complexity-theoretic NP-hardness is lacking. Researchers at MIT describe a new approach for algorithmic intractability in random structures, which is based on the topological disconnectivity property of the set of pairwise distances of near-optimal solutions, called the Overlap Gap Property. The article demonstrates how this property 1) emerges in most models known to exhibit an apparent algorithmic hardness; 2) is consistent with the hardness/tractability phase transition for many models analyzed to the day; and, importantly, 3) allows to mathematically rigorously rule out a large class of algorithms as potential contenders, specifically the algorithms that exhibit the input stability (insensitivity)…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
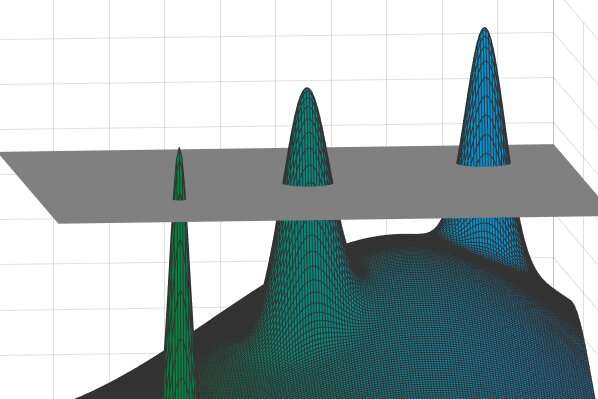
In some cases, the diameter of each peak will be much smaller than the distances between different peaks… there would be a telltale “gap” in these distances… Credit: David Gamarnik et al.