Phys.org October 8, 2021
Rechargeable magnesium and calcium metal batteries (RMBs and RCBs) are promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries because of the high crustal abundance and capacity of magnesium and calcium. But they are plagued by sluggish kinetics and parasitic reactions. A team of researchers in the US (USA – University of Maryland, US Army, China) found a family of methoxyethyl-amine chelants that greatly promote interfacial charge transfer kinetics and suppress side reactions on both the cathode and metal anode through solvation sheath reorganization, thus enabling stable and highly reversible cycling of the RMB and RCB full cells with energy densities of 412 and 471 watt-hours per kilogram, respectively. The work provides a versatile electrolyte design strategy for divalent metal batteries…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE 1 , 2
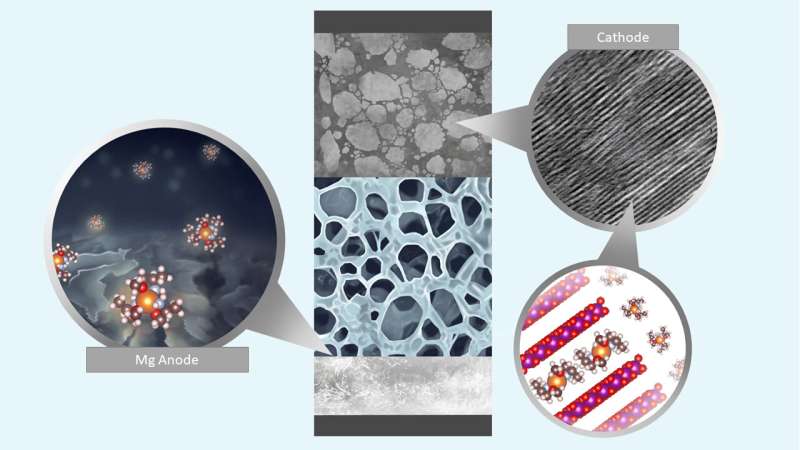
Battery electrolytes using amine-based chelants solvating divalent cations demonstrated stable and highly reversible plating/stripping of Mg metal… Credit: Nina Borodin, Singyuk Hou, Xiao Ji