Phys.org September 22, 2021
A team of researchers in the US (NIST, University of Colorado, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, University of Oregon, UT Austin) demonstrated high-fidelity laser-free universal control of two trapped-ion qubits by creating both symmetric and antisymmetric maximally entangled states with fidelities of 1+0−0.0017 and 0.9977+0.0010−0.0013, respectively (68 per cent confidence level), corrected for initialization error. They used a scheme based on radiofrequency magnetic field gradients combined with microwave magnetic fields that is robust against multiple sources of decoherence and usable with essentially any trapped ion species. The scheme has the potential to perform simultaneous entangling operations on multiple pairs of ions in a large-scale trapped-ion quantum processor without increasing control signal power or complexity. Combining this technology with low-power laser light delivered via trap-integrated photonics and trap-integrated photon detectors for qubit readout could provide an opportunity for scalable, high-fidelity, fully chip-integrated trapped-ion quantum computing…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
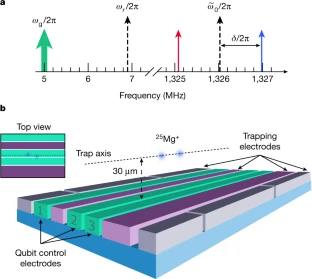
Experimental setup. Credit: Nature volume 597, pages209–213 (2021)