Phys.org August 18, 2021
Antiferromagnet is a promising candidate for developing the next generation of information technology. An international team of researchers (Germany, Sweden, Japan, Italy) showed that domain walls play an active role in the dynamic properties of the antiferromagnet nickel oxide. The experiments revealed that magnetic waves with different frequencies could be induced, amplified, and even coupled with each other across different domains—but only in the presence of domain walls. The ability highlights the potential to actively control the propagation of magnetic waves in time and space as well as energy transfer among individual waves at the femtosecond scale. This is a prerequisite for using these materials for the ultrafast storage and processing of data. Such antiferromagnet-based data storage technologies would be several orders of magnitude faster and more energy-efficient than current ones, store and process a larger amount of data and less vulnerable to malfunctions and external manipulation since the materials have no net magnetization…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
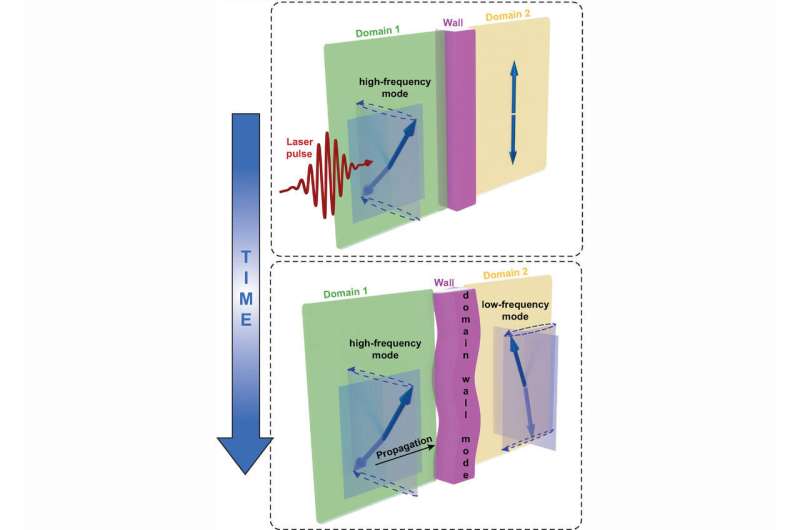
Using femtosecond laser pulses, it is possible to induce magnetic waves (coherent spin waves) in an antiferromagnetic domain (above)…Credit: Davide Bossini