Phys.org May 5, 2021
To realize the full potential of quantum computing high-fidelity information transfer mechanisms are required for quantum error correction and efficient algorithms – and that presents a major experimental challenge. A team of researchers in the US (University of Rochester, Virginia Tech, Purdue University) demonstrated adiabatic quantum state transfer (AQT) which is not affected by pulse errors and noise. They exploited entanglement even when the particles are separated by a large distance to transfer one electron’s quantum spin state across a chain of four electrons in semiconductor quantum dots. AQT is robust against pulse errors and noise. In another demonstration by implementing a series of electric-field pulses on electrons, the researchers were able to create a state similar to a time crystal and used it to transfer information between qubits. According to the researchers both AQT and time crystals, while different, could be used simultaneously with quantum computing systems to improve performance...read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE Open Access 1 , Open Access 2 , 3
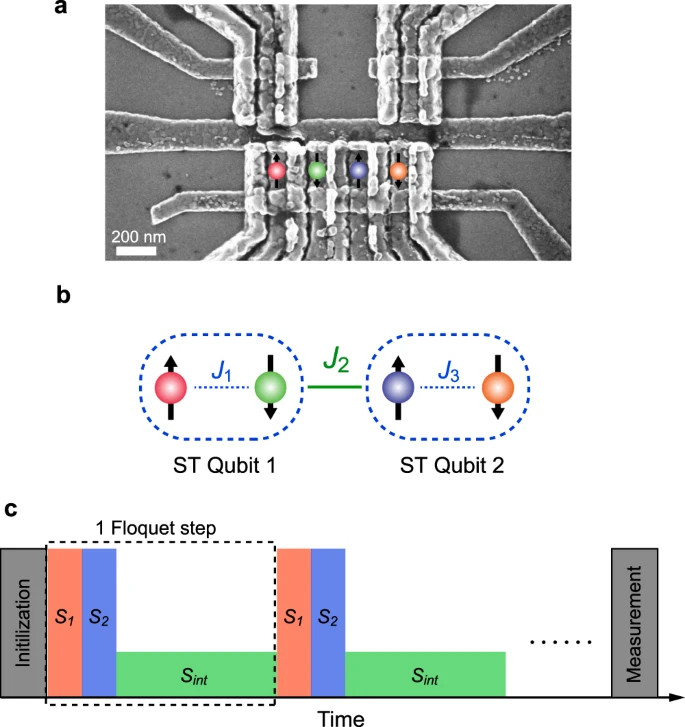
Experimental setup. Credit: Nature Communications volume 12, Article number: 2142 (2021)