EurekAlert May 10, 2021
Realizing the full potential of quantum computers requires a significant increase in the number of qubits to store and manipulate quantum information. To prevent contaminating quantum signals by thermal noise, the superconducting quantum systems must operate at ultra-low temperatures. An international team of researchers (Switzerland, India) has developed a novel approach that uses light to read out superconducting circuits. They replaced low-noise high-electron mobility transistors and coaxial cables with a lithium niobate electro-optical phase modulator and optical fibers. Microwave signals from superconducting circuits modulate a laser carrier and encode information on the output light at cryogenic temperatures. The direct conversion of microwave signals to the optical domain facilitates long-range transfer and networking between quantum systems. They demonstrated perfect agreement between optical and traditional HEMT measurements…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
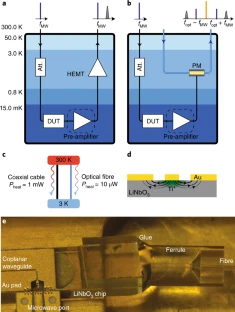
Principle of a cryogenic electro-optical interconnect for readout of superconducting devices. Credit: Nature Electronics (2021)