Phys.org April 2, 2021
Strong spin-orbit interactions make hole quantum dots central for scalable quantum computation. Therefore it is important to establish to what extent spin-orbit coupling exposes qubits to electrical noise, facilitating decoherence. Taking Ge as an example an international team of researchers (Australia, Canada) has shown that group IV gate-defined hole spin qubits generically exhibit optimal operation points, defined by the top gate electric field, at which they are both fast and long-lived: the dephasing rate vanishes to first order in the electric field noise along with all directions in space, the electron dipole spin resonance strength is maximized, while relaxation is drastically reduced at small magnetic fields. The optimal operation points are traced to group IV crystal symmetry and properties of the Rashba spin-orbit interaction unique to spin-3/2 systems. Their results suggest group IV hole spin qubits as ideal platforms for ultra-fast, highly coherent scalable quantum computing…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
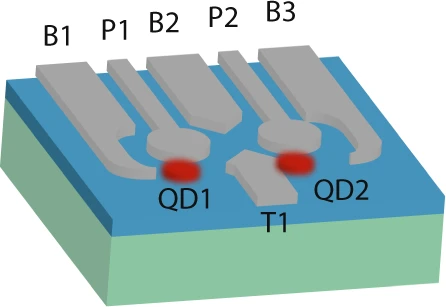
A prototype double quantum dot in a 2D hole gas. Credit: npj Quantum Information volume 7, Article number: 54 (2021)