Phys.org December 21, 2020
The goal of quantum chemistry is to predict chemical and physical properties of molecules based solely on the arrangement of their atoms in space, avoiding the need for resource-intensive and time-consuming laboratory experiments. In principle, this can be achieved by solving the Schrödinger equation. Up to now, it has been impossible to find an exact solution for arbitrary molecules that can be efficiently computed. To solve this problem researchers in Germany have proposed PauliNet, a deep-learning wavefunction ansatz that achieves nearly exact solutions of the electronic Schrödinger equation for molecules with up to 30 electrons. PauliNet incorporates the physics of valid wavefunctions and is trained using variational quantum Monte Carlo. It outperforms previous state-of-the-art variational ansatzes for atoms and matches the accuracy of highly specialized quantum chemistry methods on the transition-state energy of cyclobutadiene, while being computationally efficient. The research opens a new approach for the molecular and material sciences …read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
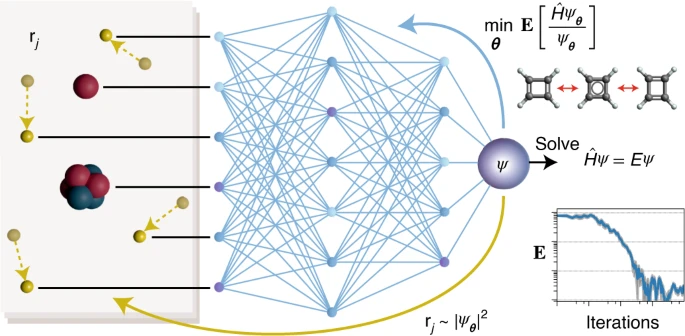
Abstract. Credit: Nature Chemistry volume 12, pages891–897(2020)