EurekAlert November 13, 2020
Current technology in LiDARS bounces the laser beams off moving mirrors, a mechanical method that results in slower scanning speeds and inaccuracies. Researchers in Japan have developed a new beam scanning device utilizing ‘photonic crystals’ whose lattice points can be arranged as nanoscale antennae. They found that by adjusting both position and size resulted in a seemingly random photonic crystal, producing an accurate beam without power loss. They called this a ‘dually modulated photonic crystal’. They showed that the scanner can generate beams in one hundred different directions: a resolution of 10×10. With further refinements, the resolution could be increased by a factor of 900: up to a 300×300 resolution range. They expect to develop a LiDAR system small enough to hold on a fingertip…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
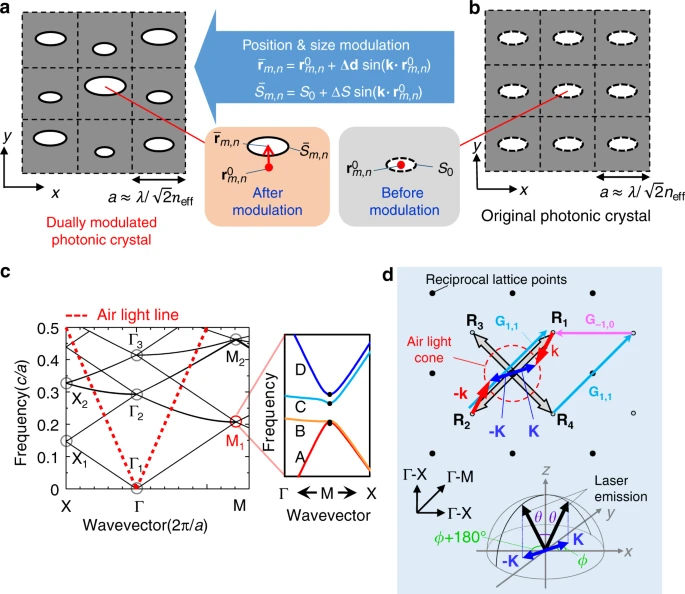
Dually modulated photonic crystal for laser beam scanning. Credit: Nature Communications volume 11, Article number: 3487 (2020)