Nanowerk July 8, 2020
Using laser-induced, extremely high-frequency ultrasound researchers in the Netherlands detected diffraction gratings buried below a stack of tens of 18-nm-thick SiO2 and Si3N4 layers and an optically opaque metal layer. The shape and amplitude of a buried metal grating were encoded on the spatial phase of the reflected acoustic wave. They showed that the complex shape of the diffracted signal as a function of time can be reproduced using a comprehensive numerical model that includes the generation, propagation, and optical detection of the acoustic waves. The results show that laser-induced ultrasound is a promising technique for subsurface nanometrology applications…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
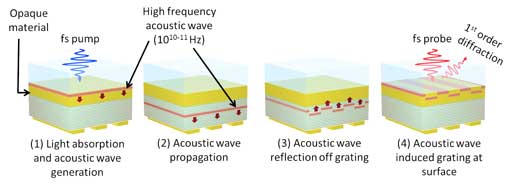
A femtosecond pump laser ‘knocks’ at the opaque material… Credit: ARCNL