Phys.org April 14, 2020
The optimal operation of electrothermal elements relies on mastering two competing boundary conditions: the maximization of the electrothermal response and the blockade of lattice (phonon) thermal conduction. Researchers in Finland proposed and demonstrated that efficient electrothermal operation and phonon blocking can be achieved in solid-state thermionic junctions, paving the way for new phonon-engineered high-efficiency refrigerators and sensors. For demonstration they used semiconductor-superconductor (Sm-S) junctions where the electrothermal response arises from the superconducting energy gap and the phonon blocking results from the acoustic transmission bottleneck at the junction. They demonstrated a cooling platform where a silicon chip cooled by ~40% from the bath temperature and how the observed effect can be used in radiation detectors and multistage electronic refrigerators suitable for cooling of quantum technology devices…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
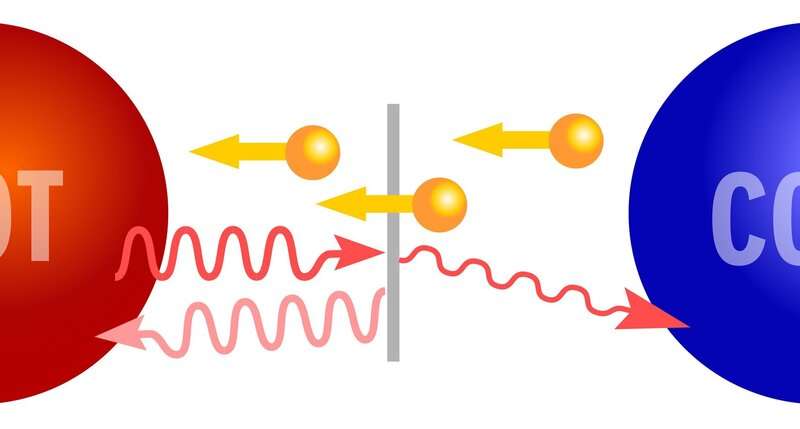
Credit: VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland