Phys.org March 19, 2020
A team of researchers in the US (Duke University, Michigan State University, MIT) has demonstrated a robust and high-performance stretchable electrode based on biaxially crumpled Au-coated carbon nanotube forest. It has nearly identical electrochemical performance at different measured charge/discharge rates under different strain conditions and a maximum specific capacitance of ∼6 mF cm−2 at the current density of 40 mA cm−2 under large strains, exhibiting superior mechanical and electrochemical stability. The researchers envision the supercapacitor being part of a power-independent, stretchable, flexible electronic system for applications such as wearable electronics or biomedical devices…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
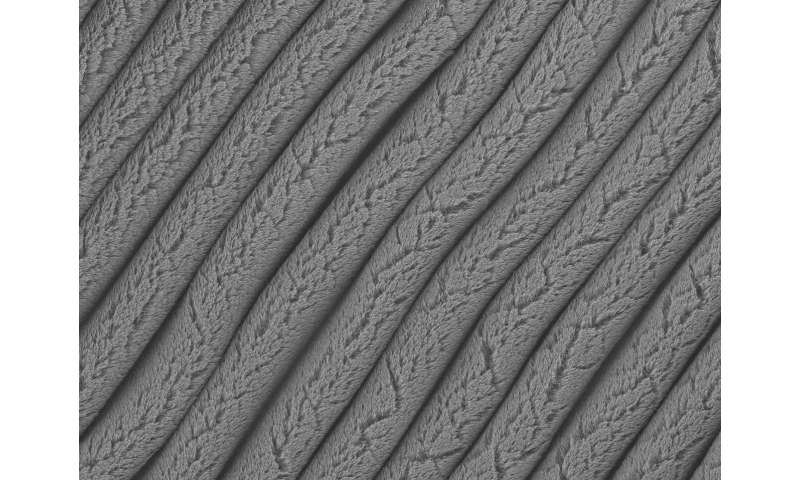
These forest-like rows of carbon nanotubes were created on an elastomer substrate that was pre-stretched in one direction and then allowed to contract. Credit: Changyong Cao, Michigan State University