Science Daily January 22, 2020
Biomass burning, which occurs on a large-scale during wildfires and some controlled burns, is a major source of air pollutants that impact air quality, human health, and climate. Particulate matter with a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers (PM2.5) has been shown to have particularly serious health effects when inhaled. Researchers at Yale University monitored the air quality at 5 sites in Cnnecticut and New York metropolitan area. In August of 2018, they observed two spikes in the presence of air pollutants found in the smoke of wildfires and controlled agricultural burning. Using data from the observation sites, smoke maps from satellite imagery, and backtracking 3-D models of air parcels they traced the pollutants’ origin to fires on the western coast of Canada, and the southeastern U.S. According to the researchers increased understanding of long-distance transport is critical for predicting and managing air quality health risks in smoke-impacted areas…read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
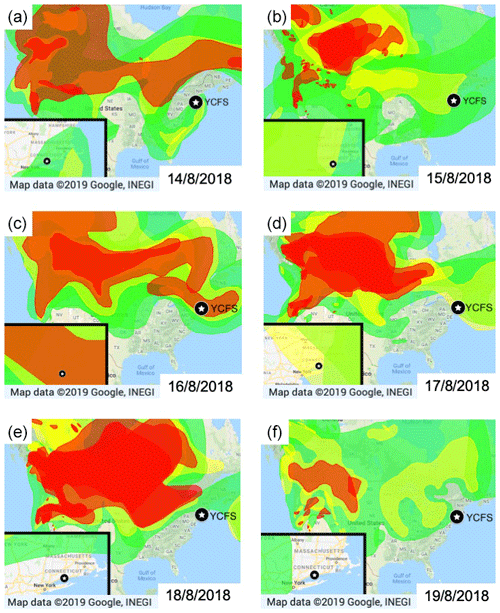
Smoke maps(NOAA) based on satellite imagery… Credit: Atmos. Chem. Phys., 20, 671–682, 2020