Phys.org August 28, 2019
An international team of researchers (China, USA – Louisiana State University, Texas A&M University, Baylor University, Princeton University, Germany, UK) conducted an experiment to test quantum interference, entanglement, and nonlocality using two dissimilar photon sources, the Sun and a semiconductor quantum dot on the Earth, which are separated by approximately 150 million km. By making the photons indistinguishable in all degrees of freedom, they observed time-resolved two-photon quantum interference with a raw visibility of 0.796, well above the 0.5 classical limit, providing unambiguous evidence of the quantum nature of thermal light. Using the photons with no common history, they demonstrated postselected two-photon entanglement with a state fidelity of 0.826 and a violation of Bell inequality by 2.20. The experiment can be further extended to a larger scale using photons from distant stars and open a new route to quantum optics experiments at an astronomical scale…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
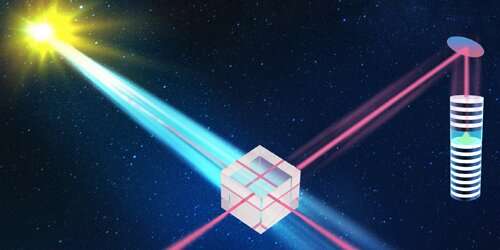
Credit: C.-Y. Lu and L.-C. Peng/HFNL