Science Daily July 22, 1019
The widespread adoption of thermoelectric devices that can directly convert electricity into thermal energy for cooling and heating has been hindered by the lack of materials that are both inexpensive and highly efficient at room temperature. A team of researchers in the US (University of Houston, MIT) has created an n-type material comprised of magnesium and bismuth. To produce a thermoelectric module using the new material, they combined it with a p-type version of the traditional bismuth-tellurium alloy. This allowed them to use just half as much tellurium as most current modules. The n-type Mg3Bi2-based materials are promising for thermoelectric cooling applications…read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
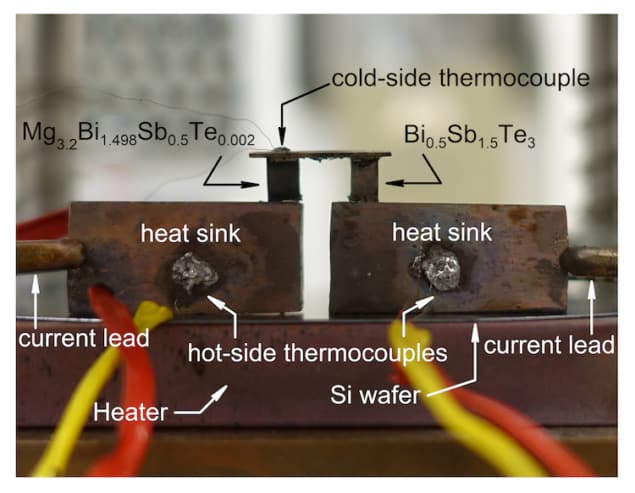
Experimental setup for thermoelectric cooling. Courtesy: Jun Mao, University of Houston