Nanowerk July 16, 2018
To efficiently transport light on small scales, researchers in Singapore have developed a more efficient method that involves a string of cylindrical silicon nanoparticles. The first nanoparticle is excited using light and then measured the light that reaches another nanoparticle further down the line. They found the fall in the light intensity to be low. The nanoparticles are not in direct contact with each other. Instead, light is transferred to the next particle through magnetic-field resonances. Although each particle is a resonant scatterer when they are lined up they work as a single waveguide without leaking light. The team has already demonstrated the same concept at telecommunication wavelengths. They are now working on developing various on-chip photonic components based on the concept… read more. TECHNICAL ARTICLE
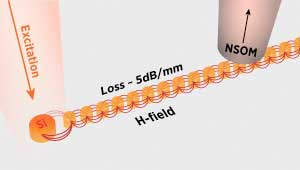
Near-field scanning optical microscope measurements have shown that cylindrical silicon nanoparticles arranged in a line can transport light with low loss due to magnetic-field resonances between them. (© ACS)