Nanowerk December 2, 2024
Researchers in South Korea developed high-performance flexible oxide thin-film transistors (TFTs) using SnO2 semiconductor and high-k ZrO2 dielectric, both formed through combustion-assisted sol-gel processes. The method involved the exothermic reaction of fuels and oxidizers to produce high-quality oxide films without extensive external heating. The combustion ZrO2 films had an amorphous structure, a higher proportion of oxygen corresponding to the oxide network, which contributed to the low leakage current and frequency-independent dielectric properties. The zirconium dioxide TFTs fabricated on flexible substrates exhibited excellent electrical characteristics, field-effect mobility, subthreshold swing, and an on/off current ratio of 1.13 × 106 at a low operating voltage of 3 V. They demonstrated flexible ZrO2/SnO2 TFTs with robust mechanical stability, capable of withstanding 5000 cycles of bending tests, and achieved by scaling down the device dimensions… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
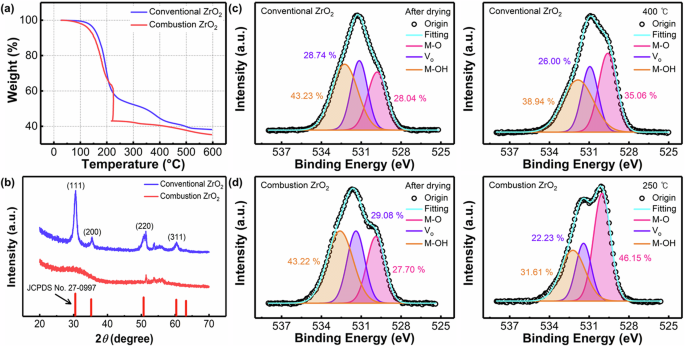
Characteristics of ZrO2 films. Credit: npj Flexible Electronics volume 8, Article number: 74, 2 November 2024