Phys.org July 26, 2024
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), which typically exhibit great toughness, have emerged as promising candidates for innovative energy storage solutions. An international team of researchers (Japan, USA – University of Maryland Baltimore County, Michigan State University, South Africa) produced SWCNT ropes wrapped in thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers, and demonstrated experimentally that a twisted rope composed of these SWCNTs possesses the remarkable ability to reversibly store nanomechanical energy. The gravimetric energy density of the twisted ropes reaches up to 2.1 MJ kg−1, exceeded the energy storage capacity of mechanical steel springs by over four orders of magnitude and surpassed advanced lithium-ion batteries by a factor of three. In contrast to chemical and electrochemical energy carriers, the nanomechanical energy stored in a twisted SWCNT rope is safe even in hostile environments. According to the researchers this energy does not deplete over time and is accessible at temperatures ranging from −60 to +100 °C… read more. Open Access TECHNICAL ARTICLE
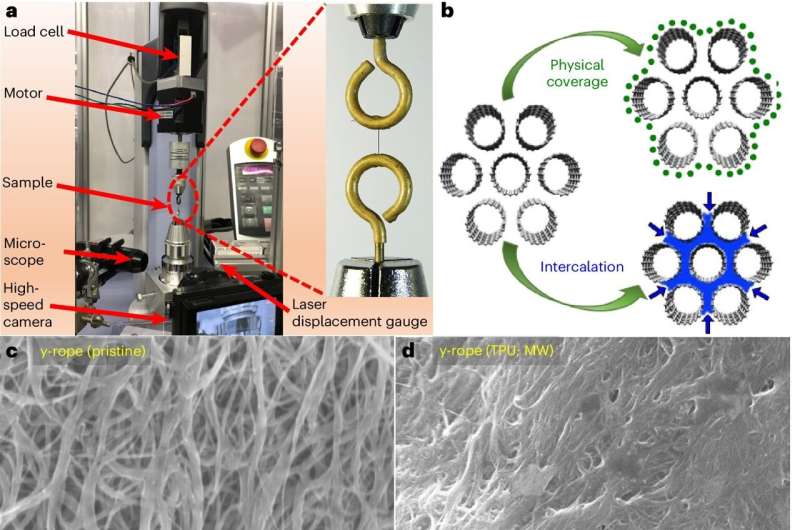
Equipment and measurement of the GED of twisted SWCNT ropes. Credit: Nature Nanotechnology, 16 April 2024